What is incontinence?
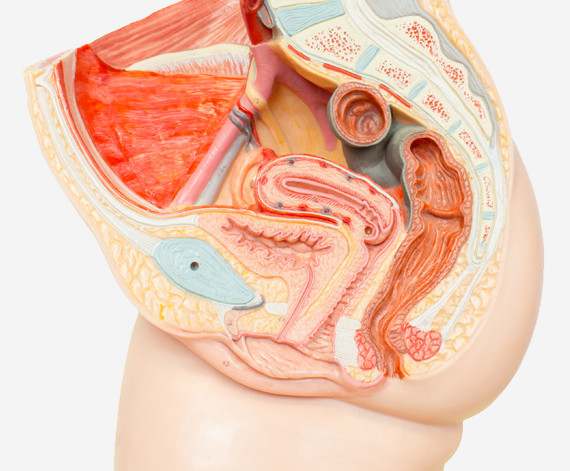
Incontinence is a term that describes any accidental or involuntary loss of urine from the bladder (urinary incontinence).
Incontinence is a widespread condition that ranges in severity from ‘a small leak’ to complete loss of bladder control. Over 4 million Australians have bladder control problems for a variety of reasons.
There are different types of incontinence with a number of possible causes. The following are the most common:
- Stress incontinence
- Urge incontinence
- Incontinence associated with chronic retention
- Functional incontinence
- True incontinence.
Stress incontinence
Stress incontinence is due to insufficient strength of the pelvic floor muscles to prevent passage of urine during activity that increases intra-abdominal pressure such as coughing, sneezing and lifting heavy objects.

Urge incontinence
Urinary urgency is a sudden, compelling urge to urinate. Incontinence occurs when you are unable to supress this until you reach a toilet.
Incontinence associated with chronic retention
Incontinence associated with chronic retention is when the bladder is unable to empty properly and frequent leakage of small amounts of urine occurs as a result.
Functional incontinence
Functional incontinence is when a person does not recognise the need to go to the toilet, does not recognise where the toilet is or is unable to get to a toilet in time. This results in passing urine in inappropriate places. Causes include dementia, poor mobility and psychiatric disorders.
True (structural) incontinence
True or structural incontinence occurs when there is an abnormal communication between the bladder and the vagina, uterus or skin. The most common cause is an acquired fistula from complicated childbirth. Urine continually leaks through this communication making you constantly wet.
KEY POINTS
- Urinary incontinence is NOT a normal part of aging.
- It is important to diagnosis the cause of the incontinence BEFORE commencing treatment.
- The cause of the incontinence may be determined by history, physical examination or medical investigations.
- There are many treatment options for urinary incontinence
